Astronomers from the US and UK have found evidence for the sort of debris associated with earth-type planetary formation around three stars - Vega, Fomalhaut and Beta Pictoris. The team used a new instrument, the submillimetre common-user bolometer array (SCUBA), at the James Clerk Maxwell telescope in Hawaii to detect the dust in the debris. The team had to observe the dust at submillimetre wavelengths because glare from the star tends to obscure any debris at optical and infrared wavelengths. The report is published in the April 23 issue of Nature.
Planets are thought to form from the debris surrounding young stars. As material rotates around the star, gravitational attraction causes the debris to clump together into planets. Gradually the planets sweep up the debris and dust in their orbit, decreasing the amount of material in the star’s rotational axis. For example, if our solar system was observed from a distance at submillimetre wavelengths, the brightest dust emissions would occur at some distance to the Sun.
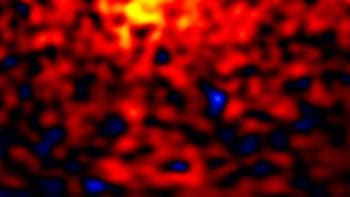
When the groups observed Fomalhaut – a young star – they found that the brightest dust emissions existed some distance away from the star. There was also a dust-free central cavity, approximately the size of Neptune’s orbit, between the star and the main emission bands. The amount of dust seen by the detector only totalled a few lunar masses, leading the researchers to believe that planetary formation has swept the material away.
Although both Vega and Beta Pictoris also have their brightest dust emissions some distance away from the main star, the astronomers found that both stars had a concentrated peak of dust emissions that appears as a ‘bright blob’ in the detector. One possible explanation is that the ‘blobs’ are dust-shrouded Jupiter-sized planets orbiting at vast distances from the star. If this is true, then our understanding of planetary formation dynamics would have to be rewritten to explain their formation.