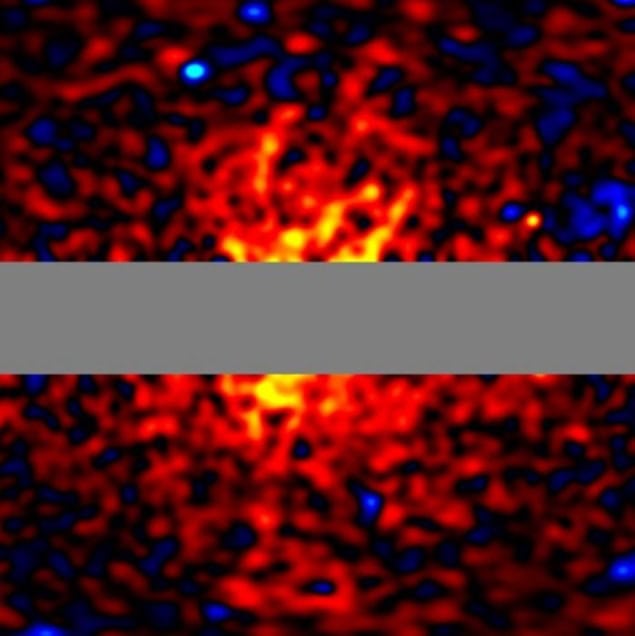
Gamma rays emitted from the halo of the Milky Way could be produced by hypothetical dark-matter particles. That is the conclusion of an astronomer in Japan who has analysed data from NASA’s Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope. The energy spectrum of the emission is what would be expected from the annihilation of particles called WIMPs. If this can be verified, it would mark the first observation of dark matter via electromagnetic radiation.
Since the 1930s astronomers have known that there is something odd about galaxies, galaxy clusters and larger structures in the universe. The problem is that there is not nearly enough visible matter in these objects to explain their dynamics and structure. A rotating galaxy, for example, should be flinging out its stars because it does not have enough self-gravitation to hold itself together.
Today, the most popular solution to this conundrum is the existence of a hypothetical substance called dark matter. Dark-matter particles would have mass and interact with each other and normal matter via the gravitational force, gluing rotating galaxies together. However, the fact that we have never observed dark matter directly means that the particles must rarely, if ever, interact via the other three forces.
Annihilating WIMPs
The weakly interacting massive particle (WIMP) is a dark-matter candidate that interacts via the weak nuclear force (or a similarly weak force). As a result of this interaction, pairs of WIMPs are expected to occasionally annihilate to create high-energy gamma rays and other particles. If this is true, dense areas of the universe such as galaxies should be sources of these gamma rays.
Now, Tomonori Totani of the University of Tokyo has analysed data from the Fermi telescope and identified an excess of gamma rays emanating from the halo of the Milky Way. What is more, Totani’s analysis suggests that the energy spectrum of the excess radiation (from about 10−100 GeV) is consistent with hypothetical WIMP annihilation processes.
“If this is correct, to the extent of my knowledge, it would mark the first time humanity has ‘seen’ dark matter,” says Totani. “This signifies a major development in astronomy and physics,” he adds.
Flattened halo of dark matter could explain high-energy ‘glow’ at Milky Way’s heart
While Totani is confident of his analysis, his conclusion must be verified independently. Furthermore, work will be needed to rule out conventional astrophysical sources of the excess radiation.
Catherine Heymans, who is Astronomer Royal for Scotland told Physics World, “I think it’s a really nice piece of work, and exactly what should be happening with the Fermi data”. The research is described in Journal of Cosmology and Astroparticle Physics. Heymans describes Totani’s paper as “well written and thorough”.




