Brachytherapy – a cancer treatment that destroys tumours using small radioactive sources implanted inside the body – plays a critical role in treating cervical cancer, offering an important option for patients with inoperable locally advanced disease. Brachytherapy can deliver high radiation doses directly to the tumour while ensuring nearby healthy tissues receive minimal dose; but its effectiveness relies on accurate delineation of the treatment target. A research team in China is using a hybrid deep-learning model to help with this task.
Planning brachytherapy treatments requires accurate contouring of the clinical target volume (CTV) on a CT scan, a task that’s traditionally performed manually. The limited soft-tissue contrast of CT, however, can result in unclear target boundaries, while applicator or needle insertion (used to deliver the radioactive sources) can deform and displace nearby organs. This makes manual contouring a time-consuming and subjective task that requires a high level of operator expertise.
Automating this process could reduce reliance on operator experience, increase workflow efficiency and improve contouring consistency. With this aim, the research team – headed up by He Ma from Northeastern University and Lin Zhang from Shanghai University of International Business and Economics – developed a 3D hybrid neural network called BCTVNet.
Currently, most brachytherapy segmentation models are based on convolutional neural networks (CNNs). CNNs effectively capture local structural features and can model fine anatomical details but struggle with long-range dependencies, which can cause problems if the target extends across multiple CT slices. Another option is to use transformer-based models that can integrate spatial information across distant regions and slices; but these are less effective at capturing fine-grained local detail.
To combine the strengths of both, BCTVNet integrates CNN with transformer branches to provide strong local detail extraction along with global information integration. BCTVNet performs 3D segmentation directly on post-insertion CT images, enabling the CTV to be defined based on the actual treatment geometry.
Model comparisons
Zhang, Ma and colleagues assessed the performance of BCTVNet using a private CT dataset from 95 patients diagnosed with locally advanced cervical cancer and treated with CT-guided 3D brachytherapy (76 in the training set, 19 in the test set). The scans had an average of 96 slices per patient and a slice thickness of 3 mm.
CT scans used to plan cervical cancer brachytherapy often exhibit unclear target boundaries. To enhance the local soft-tissue contrast and improve boundary recognition, the researchers pre-processed the CT volumes with a 3D version of the CLAHE (contrast-limited adaptive histogram equalization) algorithm, which processes the entire CT scan as a volumetric input. They then normalized the intensity values to standardize the input for the segmentation models.
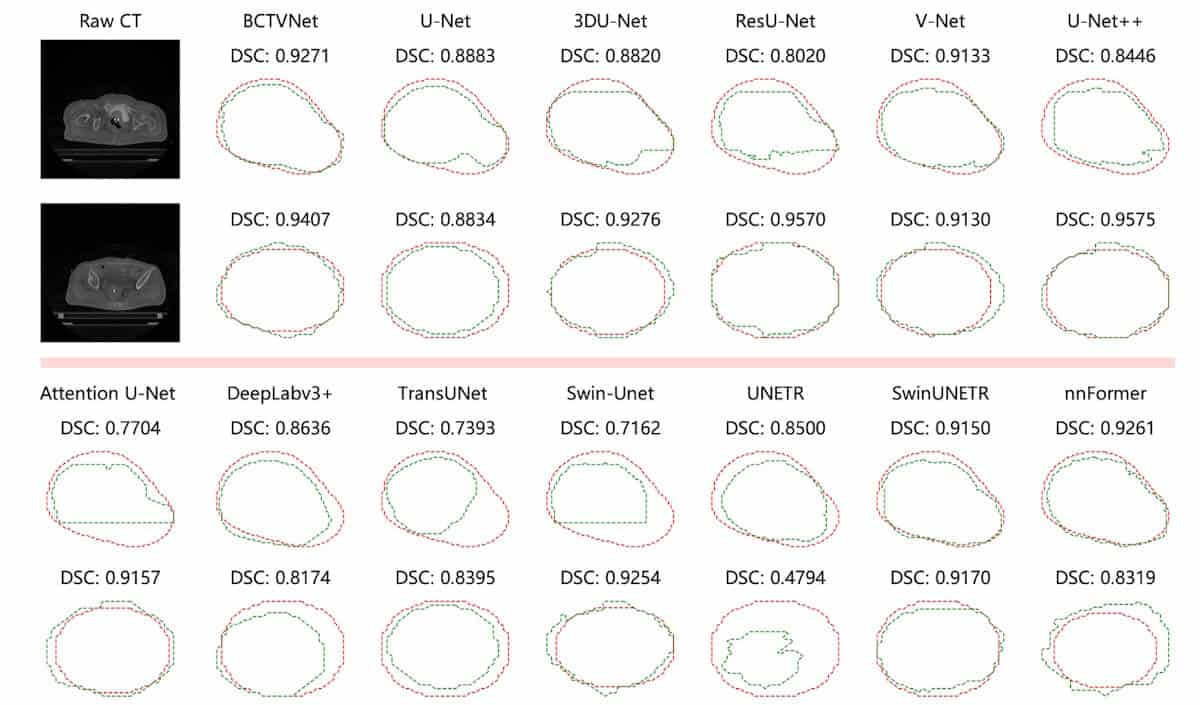
The researchers compared BCTVNet with 12 popular CNN- and transformer-based segmentation models, evaluating segmentation performance via a series of metrics, including Dice similarity coefficient (DSC), Jaccard index, Hausdorff distance 95th percentile (HD95) and average surface distance.
Contours generated by BCTVNet were closest to the ground truth, reaching a DSC of 83.24% and a HD95 (maximum distance from ground truth excluding the worst 5%) of 3.53 mm. BCTVNet consistently outperformed the other models across all evaluation metrics. It also demonstrated strong classification accuracy, with a precision of 82.10% and a recall of 85.84%, implying fewer false detections and successful capture of target regions.
Generative AI speeds medical image analysis without impacting accuracy
To evaluate the model’s generalizability, the team conducted additional experiments on the public dataset SegTHOR, which contains 60 thoracic 3D CT scans (40 for training, 20 for testing) from patients with oesophageal cancer. Here again, BCTVNet achieved the best scores among all the segmentation models, with the highest average DSC of 87.09% and the lowest average HD95 of 7.39 mm.
“BCTVNet effectively overcomes key challenges in CTV segmentation and achieves superior performance compared to existing methods,” the team concludes. “The proposed approach provides an effective and reliable solution for automatic CTV delineation and can serve as a supportive tool in clinical workflows.”
The researchers report their findings in Machine Learning: Science and Technology.