Achieving a profound understanding of any subject is hard. When that subject is quantum mechanics, it’s even harder. And when one departs from ideal theoretical scenarios and enters the real world of experimental limitations, it becomes more challenging still – yet that is what physicists at the Freie Universität Berlin (FU-Berlin), Germany recently did by exploring what happens to entanglement theory in real quantum computers. In doing so, they created a bridge between two fields that have so far largely developed in parallel: entanglement theory (rooted in physics) and computational complexity (rooted in computer science).
Ebits, the standard currency of entanglement
In quantum mechanics, a composite system is said to be entangled when its total wavefunction cannot be written as a product of the states of its individual subsystems. This leads to correlations between subsystems that arise from the structure of the quantum state, not from any shared classical information. Many speed-ups achieved in quantum computing, quantum cryptography and quantum metrology rely heavily on entanglement, but not every form of entanglement is equally useful. Only specific kinds of entanglement will enable a given computational or communication task.
To make quantum technologies practical, the available entangled resources must therefore often be converted into forms suitable for specific applications. One major conversion process involves transforming partially entangled states into, or extracting them from, the maximally entangled bit (ebit) that acts as the standard unit of entanglement. High-fidelity ebits – entangled pairs that are extremely close to the ideal perfectly entangled state – can be distilled from noisy or imperfect entangled states through entanglement distillation, while entanglement dilution allows one to reconstruct the desired entangled states from purified ebits.
In an idealized setting, with an infinite number of copies of entangled states and unlimited computational power, a single quantity called the von Neumann entropy fully determines how many ebits can be extracted or are required. But reality is far less forgiving: we never have infinite resources, and computational power is always limited, just like we don’t have an infinite amount of gold on Earth.
Entanglement under finite resources
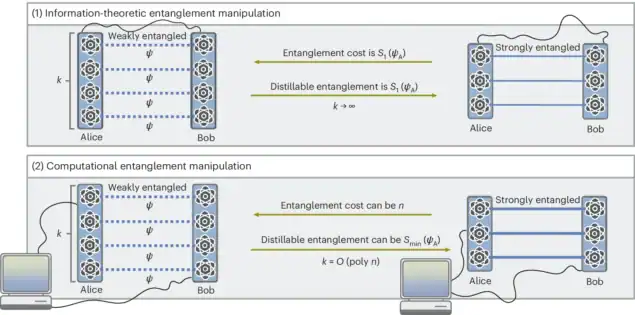
In the present work, which is published in Nature Physics, the FU-Berlin team of Lorenzo Leone, Jacopo Rizzo, Jens Eisert and Sofiene Jerbi asked what happens when these ideal assumptions break down. They study the case where only a finite number of entangled states, which can scale at most polynomially with the number of quantum bits (qubits) in the system, are considered and all local operations and classical communication (LOCC) are performed in a finite polynomial time.
They found that the simple correspondence between von Neumann entropy and extractable or required ebits no longer holds: even when a state has a large von Neumann entropy, the number of ebits that can be efficiently extracted may be much lower. In these cases, the number is bounded instead by the min-entropy of the reduced state (an operational measure determined solely by the state’s largest eigenvalue that captures how much entanglement can be reliably distilled from a single copy of the state) without averaging over many uses. On the other hand, even a state with negligible von Neumann entanglement may require a maximal ebit budget for efficient dilution.
Leone and Eisert say they were inspired to perform this study by recent work on so-called pseudo-entangled states, which are states that look at lot more entangled than they are for computationally bounded observers. Their construction of pseudo-entangled states highlights a dramatic worst-case scenario: a state that appears almost unentangled by conventional measures may still require a large number of ebits to create it efficiently. The takeaway is that computability matters, and quantum resources you might have thought were available may be, in effect, locked away simply because they cannot be processed efficiently. In other words, practical limitations make the line between a “resource” and a “usable resource” even sharper.
Quantum resources in a limited world
The researchers say that their study raises multiple questions for future exploration. One such question concerns whether a similar computational‐efficiency gap exists for other quantum resources such as magic and coherence. Another is whether one can build a full resource theory with complexity constraints, where quantities reflect not just what can be converted, but how efficient that conversion is.
Distillation method strengthens quantum entanglement in a single pair of photons
Regardless of the answers, the era of entanglement under infinite book‐keeping is giving way to an era of entanglement under limited books, limited clocks and limited gates. And in this more realistic space, quantum technologies may still shine, but the calculus of what can be done and what can be harnessed needs a serious retooling.