Graphene soaks up arsenic
'Wonder material' could help purify water
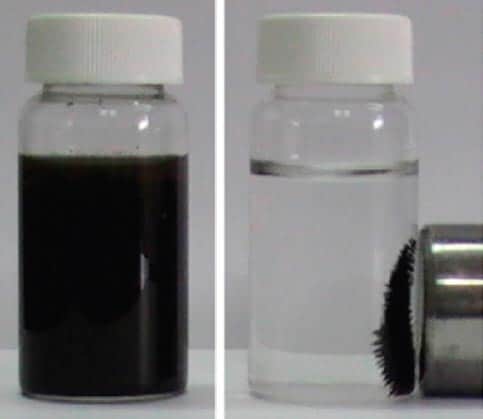 Read article: Graphene soaks up arsenic
Read article: Graphene soaks up arsenic
Thank you for registering with Physics World
If you'd like to change your details at any time, please visit My account
Isabelle Dumé is a contributing editor to Physics World. She has more than 10 years of experience in science writing and editing in condensed-matter physics relating to technology/nanotechnology/biotechnology, astronomy and astrophysics, energy and the environment, biology and medicine. She has an MSc in advanced materials and a PhD in magnetism. In her spare time, she helps to organize cafés scientifiques.
 Read article: Graphene soaks up arsenic
Read article: Graphene soaks up arsenic
New devices can be driven by any simple light source
 Read article: Efficient nano motor cleverly harnesses light
Read article: Efficient nano motor cleverly harnesses light
Current efficiency limits of 30% could be vastly improved by capturing 'hot electrons'
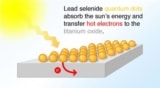 Read article: Quantum dots for highly efficient solar cells
Read article: Quantum dots for highly efficient solar cells
Improving the effectiveness of electrodes
 Read article: Nanotubes boost battery performance
Read article: Nanotubes boost battery performance
New technique could make flexible electronic circuits
 Read article: AFM tip ‘writes’ graphene nanowires
Read article: AFM tip ‘writes’ graphene nanowires
'Entangled' LED could help make quantum computer
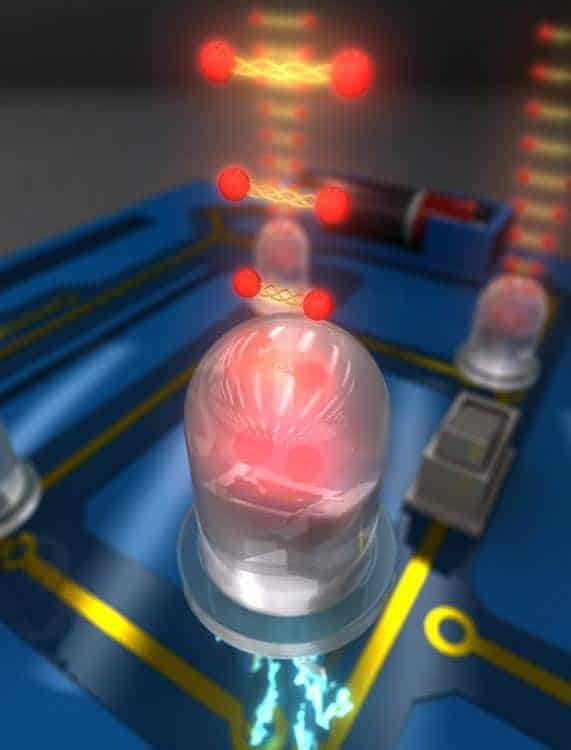 Read article: Entangling photons with electricity
Read article: Entangling photons with electricity
Technique for patterning graphane with quantum dots
 Read article: A liberal sprinkling of quantum dots
Read article: A liberal sprinkling of quantum dots
Force measurements could lead to better nanowires
Carbon multi-layers could chill chips
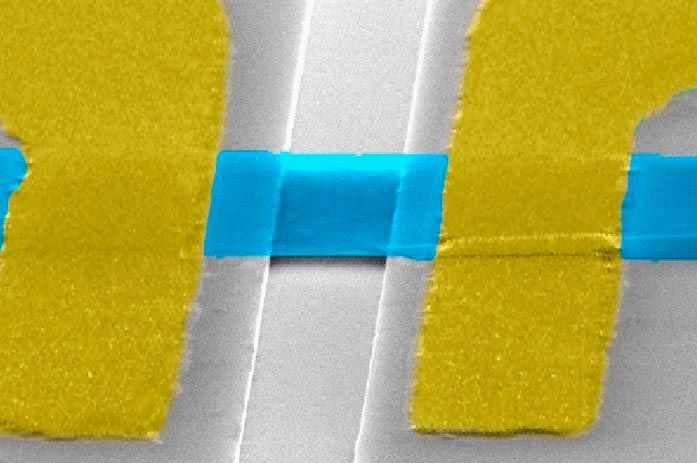 Read article: ‘Few-layer’ graphene keeps its cool
Read article: ‘Few-layer’ graphene keeps its cool
Carbon and gold join forces in photonic metamaterial
 Read article: Nanotube ‘fuzz’ boosts optical performance
Read article: Nanotube ‘fuzz’ boosts optical performance