Author
Array
(
[0] => linkedin
[1] => facebook
[2] => twitter
[3] => google-plus
[4] => youtube
)
Array
(
[0] => linkedin
[1] => facebook
[2] => twitter
[3] => google-plus
[4] => youtube
)
Array
(
[0] => linkedin
[1] => facebook
[2] => twitter
[3] => google-plus
[4] => youtube
)
Array
(
[0] => linkedin
[1] => facebook
[2] => twitter
[3] => google-plus
[4] => youtube
)
Array
(
[0] => linkedin
[1] => facebook
[2] => twitter
[3] => google-plus
[4] => youtube
)
No Author
Author archive
 Read article: PhDs are worth more for women
Read article: PhDs are worth more for women
With the new academic year about to begin, undergraduate students will soon be thinking about whether to apply for a PhD. Doing a doctorate can, of course, be a very rewarding experience. It allows students to mature as independent scientists and to experience cutting-edge research – both within their own departments and at prestigious international […]
 Read article: Physicists push themselves to the limit
Read article: Physicists push themselves to the limit
Frost bite, no toilets and polar bears - these are some of the hazards that physicists face when working in hostile environments. But, as Paula Gould reports, they seem to enjoy it
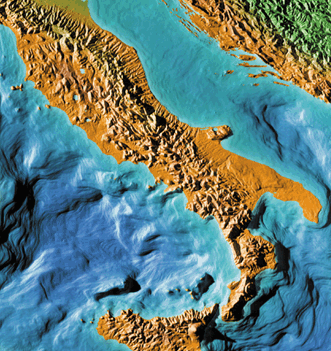 Read article: Returning to the Fermi level
Read article: Returning to the Fermi level
There is no doubt that Italy is a world force in physics. When the nations of the world are ranked by the number of physics papers that they publish, Italy is sixth. It also makes the top ten when nations are ranked by the impact of their papers as measured by citations in other publications. […]
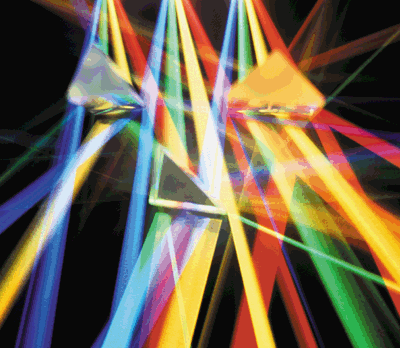 Read article: Rewriting the laws of optics
Read article: Rewriting the laws of optics
New experiments are pushing our understanding of light and optics to the limit and are also opening up new areas of physics and novel applications
 Read article: Taming light with cold atoms
Read article: Taming light with cold atoms
The ability to stop light in its tracks by passing it through a cloud of ultracold atoms could lead to new techniques for optical storage
 Read article: The quest for the Northern Lights
Read article: The quest for the Northern Lights
The Northern Lights is a well researched biographical tale of the Norwegian physicist and genius Kristian Birkeland, whose life was spent exclusively in pursuit of the scientific goal of understanding solar-terrestrial relationships. The author, Lucy Jago, has turned his life into a highly compelling story that keeps the reader interested, and also learning, as the […]
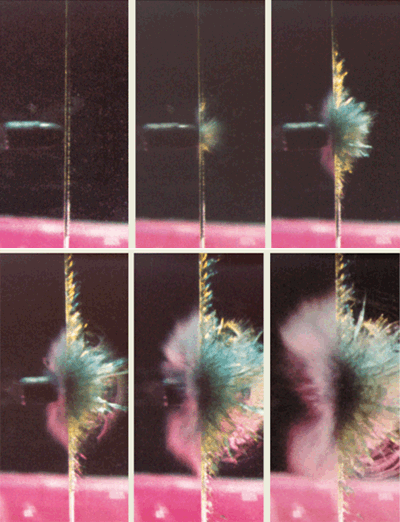 Read article: Ultrafast cameras streak ahead
Read article: Ultrafast cameras streak ahead
According to the old adage, “a picture paints a thousand words”. And in many scientific disciplines ultrahigh-speed imaging is the only reliable way to visualize the countless physical and mechanical processes that occur on microsecond timescales. Such processes include ballistics, the propagation of cracks in materials, flame fronts in combustion research, the generation of shock […]

First discovered in experiments on ions in the early 1920s, the understanding of magnetic moments played a central role in theoretical physics during the 20th century. In the case of free electrons, comparisons between theory and experiments of ever-increasing accuracy continue to provide one of the most significant tests of the theory of quantum electrodynamics. […]

Cystal impurities in silicon can now be controlled to the level of one part in a billion, while major faults in the crystalline structure can be avoided. As techniques to control its growth have developed, the applications of silicon have been pushed in new directions. In addition, there is a constant drive to improve light […]
 Read article: Six of the best for gravitational lens
Read article: Six of the best for gravitational lens
A distant galaxy is imaged six times by the strong gravity of a galactic cluster
Copyright © 2025 by IOP Publishing Ltd and individual contributors
 Read article: PhDs are worth more for women
Read article: PhDs are worth more for women







