Author
Array
(
[0] => linkedin
[1] => facebook
[2] => twitter
[3] => google-plus
[4] => youtube
)
Array
(
[0] => linkedin
[1] => facebook
[2] => twitter
[3] => google-plus
[4] => youtube
)
Array
(
[0] => linkedin
[1] => facebook
[2] => twitter
[3] => google-plus
[4] => youtube
)
Array
(
[0] => linkedin
[1] => facebook
[2] => twitter
[3] => google-plus
[4] => youtube
)
Array
(
[0] => linkedin
[1] => facebook
[2] => twitter
[3] => google-plus
[4] => youtube
)
No Author
Author archive
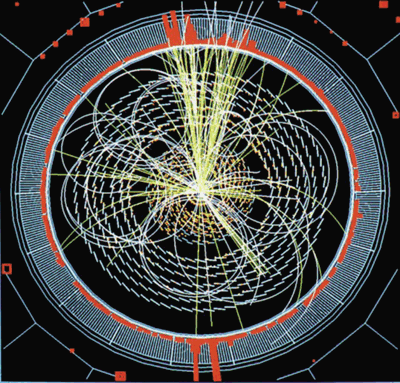 Read article: Supersymmetry makes its case
Read article: Supersymmetry makes its case
In 1951 Herman Weyl, a pioneer in the application of the mathematics of symmetry to physics, published a popular account of the field. His book was called, quite simply, Symmetry. To the uninitiated, Gordon Kane’s new book Supersymmetry might be construed as evidence that the world of physics has been gripped by the same inflationary […]
 Read article: Women matter
Read article: Women matter
What do the evolution of the universe and the relative proportions of men and women in physics have in common? Well, imagine that men are matter and that women are antimatter. And note that equal amounts of matter and antimatter were created in the big bang, just as equal numbers of baby boys and girls […]
 Read article: Physics, technology and the Olympics
Read article: Physics, technology and the Olympics
What effect does technology have on the performance of athletes, asks Steve Haake
 Read article: Science centres face the future
Read article: Science centres face the future
The UK is about to experience an explosion in the number of new interactive science centres. By this time next year about a dozen major new science-centre projects will have opened (see table). These large-scale capital schemes have been funded by a mixture of National Lottery grants from the Millennium Commission and money from public […]
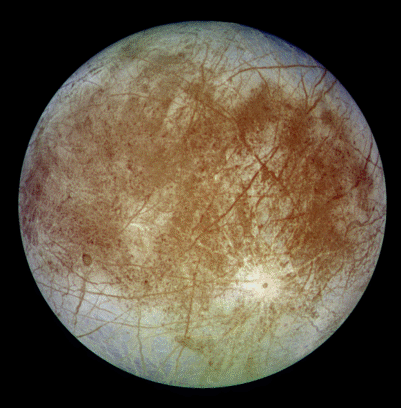 Read article: Europa: water, water everywhere
Read article: Europa: water, water everywhere
The latest evidence comes from an analysis of the magnetic fields surrounding Europa. When a conducting body is placed inside a time-varying magnetic field, electrical currents are induced inside the conductor, which in turn produce measurable secondary magnetic fields. In this case the conductor is Europa and the magnetic field is the magnetosphere of Jupiter. […]

Argon is the lightest yet of the inert gases to have formed a compound. It is difficult to persuade light inert gases to react because their outer electrons are shielded less from the electrostatic pull of the nucleus by the inner electrons that are present in heavier noble gases. Khriachtchev and co-workers created the new […]

The expansion of the universe means that the light from distant galaxies is red-shifted when observed on Earth. The larger the red shift, the greater the distance to the galaxy. Moreover, when we view a galaxy with a high redshift, we are seeing it as it was billions of years ago. By measuring the red […]

Sandage is best known for his efforts to pin down the values of the Hubble constant, the age of the Universe and its deceleration parameter through observations. Peebles is a theoretical cosmologist who has worked on problems ranging from light-element synthesis to the nature of dark matter. The awards will be presented at the Pontifical […]

Hendrik Schon, Christian Kloc and Batlogg investigated three different acenes: anthracene (which contains three linked rings), tetracene (four) and pentacene (five). The crystals are normally insulating, but when a thin layer of the material was included in a field-effect transistor, it became superconducting. The superconducting transition temperature ranged from 2 Kelvin for pentacene to 4 […]

Bernard Yurke from Lucent Technologies in the US, Andrew Turberfield from Oxford University in the UK and Lucent, and co-workers constructed the tweezers from three separate strands of DNA. DNA molecules are chains of four different bases – adenine, cytosine, guanine and thymine. Adenine will only bind to thymine, and cytosine will only bind to […]
Copyright © 2025 by IOP Publishing Ltd and individual contributors
 Read article: Supersymmetry makes its case
Read article: Supersymmetry makes its case




