
Research could lead to a standard for chemical potential
Reducing atom loss and re-using already-measured atoms enables more complex quantum computations
Quantum simulator enables scientists to test laws of transport phenomena at the quantum level
Explosive technique images collective quantum fluctuations
New atom-by-atom technique demonstrated for the first time with nobelium might ensure that elements at the bottom of the table are grouped correctly
Single ultracold atoms act as slits, stripping away noise and emphasizing the fundamental nature of wave–particle duality
Experiment could help reveal why there is so little antimatter in the universe
New "erasure correction cooling" method stores quantum information in atoms’ motional states
Although it hasn’t detected dark matter yet, its developers say it offers an alternative path that is worth exploring
A step-by-step guide to publishing your research paper. Helping you get published and make an impact in your scientific community

Innovative imaging technique reveals real space correlations between atoms in quantum systems
 Read article: Physicists take ‘snapshots’ of quantum gases in continuous space
Read article: Physicists take ‘snapshots’ of quantum gases in continuous space
Antiprotons could be next after CERN scientists demonstrate transport of trapped particles on a truck
 Read article: Protons take to the road
Read article: Protons take to the road
Efimov states could be used to build molecules and achieve nuclear fusion
 Read article: Five-body recombination could cause significant loss from atom traps
Read article: Five-body recombination could cause significant loss from atom traps
Result could force a rethink on basic models of dark matter, say researchers
 Read article: Plasma physics sets upper limit on the strength of ‘dark electromagnetism’
Read article: Plasma physics sets upper limit on the strength of ‘dark electromagnetism’
Radiation affects quantum states of carbon monoxide
 Read article: Microwaves slow down chemical reactions at low temperatures
Read article: Microwaves slow down chemical reactions at low temperatures
Proposal would explore macroscopic quantum phenomena in many-body systems
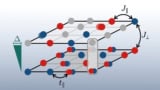 Read article: Bilayer optical lattices could unravel the secret of high-temperature superconductivity
Read article: Bilayer optical lattices could unravel the secret of high-temperature superconductivity
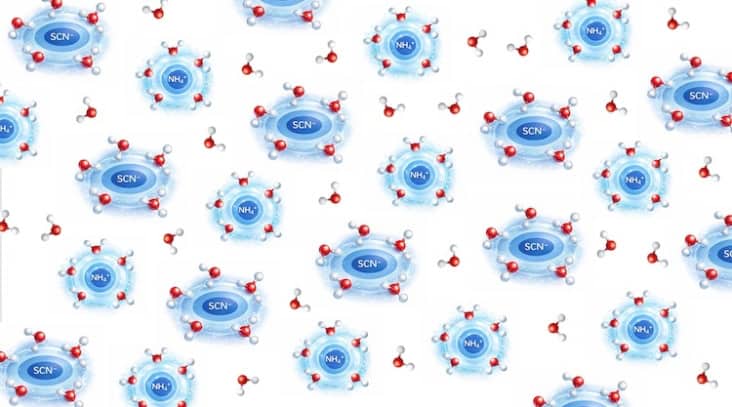
Flips in the orientation of water molecules explain sluggish reaction speeds
 Read article: Splitting water takes more energy than theory predicts – and now scientists know why
Read article: Splitting water takes more energy than theory predicts – and now scientists know why
New technique uses black-body radiation to make direct measurements with low uncertainty
 Read article: Thermometer uses Rydberg atoms to make calibration-free measurements
Read article: Thermometer uses Rydberg atoms to make calibration-free measurements
Further research could shed light on neutron-star glitches
 Read article: Quantized vortices seen in a supersolid for the first time
Read article: Quantized vortices seen in a supersolid for the first time
IOP Publishing's journal, Plasma Science and Technologies explores the knowns and unknowns of negative triangularity and evaluate its future as a power plant solution
 Read article: Negative triangularity tokamaks: a power plant plasma solution from the core to the edge?
Read article: Negative triangularity tokamaks: a power plant plasma solution from the core to the edge?
New cooling technique could help reveal physics beyond the Standard Model
 Read article: Positronium gas is laser-cooled to one degree above absolute zero
Read article: Positronium gas is laser-cooled to one degree above absolute zero
Colorado-based researchers have reduced the systematic uncertainty in their optical lattice clock to a record low. Ali Lezeik explains how they did it
 Read article: The most precise timekeeping device ever built
Read article: The most precise timekeeping device ever built
The behaviour of photons confined inside three-dimensional cavity superlattices is much more complex than that of electrons in conventional solid-state materials
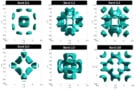 Read article: Photonic orbitals shape up
Read article: Photonic orbitals shape up
Producing fast-moving "fireballs" in the lab could shed light on processes in extreme astrophysical emissions
 Read article: Scientists create space plasmas at CERN
Read article: Scientists create space plasmas at CERN
Gravity measurement benefits from optical lattice
 Read article: Matter-wave interferometry puts new limits on ‘chameleon particles’
Read article: Matter-wave interferometry puts new limits on ‘chameleon particles’
The first observation of a promethium complex in solution represents a significant advance in rare-earth research
 Read article: Scientists uncover hidden properties of rare-earth element promethium
Read article: Scientists uncover hidden properties of rare-earth element promethium
The surface of a Kuiper Belt object called Arrokoth is rich in glucose, ribose and other sweet molecules
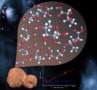 Read article: Scientists identify a ‘sugar world’ beyond Neptune
Read article: Scientists identify a ‘sugar world’ beyond Neptune