
Device works by monitoring frequency of sound waves propagating through a kagome material
New use for photolithography could have applications for data storage
Calculations explain curious properties of some 2D materials
New device could help us better understand phenomena from ocean waves and hurricanes to weather and climate
Topological kagome tubes isolate vibrations to one end, keeping the other end safe
Superconducting germanium could find application in a new generation of quantum devices
Bulk conductivity may have been hiding the dynamics of surface charge transfer, say researchers
New alloy is made by doping scandium into the well-known La-H binary system
Rayleigh–Taylor instability responsible for mushroom clouds appears in a two-component BEC
Whether you’re still working out your career pathway or have a specific role in mind, we’re here to help. Bringing a diverse range of opportunities for jobseekers at all career stages, we’ll help you take the next step in your career and find your perfect job.

Physicists have designed a protocol to study high-temperature superconductivity on an experimentally realizable platform
 Read article: New protocol makes an elusive superconducting signature measurable
Read article: New protocol makes an elusive superconducting signature measurable
Low-energy electron emission spectra depend on sample thickness
 Read article: Doorway states spotted in graphene-based materials
Read article: Doorway states spotted in graphene-based materials
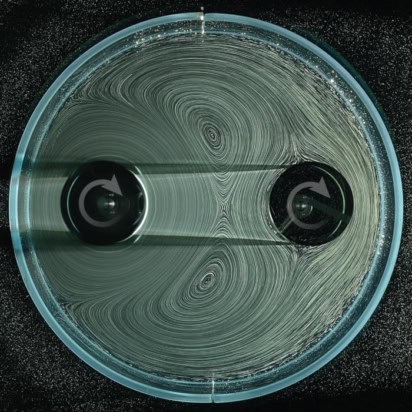
New experiments and calculations could improve aerosol and microfluidic technologies while shedding more light on airborne disease transmission
 Read article: Physicists explain why some fast-moving droplets stick to hydrophobic surfaces
Read article: Physicists explain why some fast-moving droplets stick to hydrophobic surfaces
Researchers in Japan have succeeded in switching a manganese-tin nanodot using electric current pulses as short as 0.1 ns
 Read article: Antiferromagnets could be better than ferromagnets for some ultrafast, high-density memories
Read article: Antiferromagnets could be better than ferromagnets for some ultrafast, high-density memories
Physicists model vacuum tunnelling in a simple system
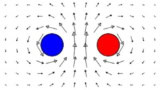 Read article: Schwinger effect appears in a 2D superfluid
Read article: Schwinger effect appears in a 2D superfluid
Effect could come in useful for a host of practical applications that call for fluid control
 Read article: Meniscus size and shape affect how liquid waves move through barriers
Read article: Meniscus size and shape affect how liquid waves move through barriers
Accessible systems is classical and operates at room temperature
 Read article: Space–time crystal emerges in a liquid crystal
Read article: Space–time crystal emerges in a liquid crystal
Observation of the Meissner effect could spur the development of highly sensitive quantum detectors that operate under high-pressure conditions
 Read article: Quantum sensors reveal ‘smoking gun’ of superconductivity in pressurized bilayer nickelates
Read article: Quantum sensors reveal ‘smoking gun’ of superconductivity in pressurized bilayer nickelates
Images are the first experimental evidence of long-predicted low-energy atomic vibrations called moiré phasons in twisted 2D materials
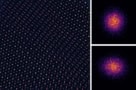 Read article: Highest-resolution images ever taken of a single atom reveal new kind of vibrations
Read article: Highest-resolution images ever taken of a single atom reveal new kind of vibrations
Superheated gold stays solid at temperatures far beyond the predicted "entropy catastrophe"
 Read article: How hot can you make a solid before it melts?
Read article: How hot can you make a solid before it melts?
Ratcheting effect could lead to better de-icing
 Read article: Melting ice propels itself across a patterned surface
Read article: Melting ice propels itself across a patterned surface
Discovery could lift theoretical constraints on calculations achievable with certain types of topological quantum computers
 Read article: Predicted quasiparticles called ‘neglectons’ hold promise for robust, universal quantum computing
Read article: Predicted quasiparticles called ‘neglectons’ hold promise for robust, universal quantum computing
Machine-learning-based molecular simulations reveal unexpected crystallization pathway
 Read article: Graphite ‘hijacks’ the journey from molten carbon to diamond
Read article: Graphite ‘hijacks’ the journey from molten carbon to diamond
Simulations and experiments indicate that the low-density amorphous ice found on comets and icy moons is not, in fact, entirely amorphous
 Read article: Space ice reveals its secrets
Read article: Space ice reveals its secrets
Monte Carlo method combines billions of diagrams related to polarons
 Read article: Feynman diagrams provide insight into quasiparticles in solids
Read article: Feynman diagrams provide insight into quasiparticles in solids
Evidence for “emergent photons” seen in frustrated antiferromagnet
 Read article: Hints of a 3D quantum spin liquid revealed by neutron scattering
Read article: Hints of a 3D quantum spin liquid revealed by neutron scattering
Join the audience for a live webinar at 3 p.m. BST/10 a.m EDT on 27 August 2025
If you use or teach the Butler-Volmer equation, join us to learn the latest advances
 Read article: The Butler-Volmer equation revisited: effect of metal work function
Read article: The Butler-Volmer equation revisited: effect of metal work function
Scanning-tunnelling microscope with a superconducting tip could help uncover materials for next-generation quantum computers
 Read article: New microscopy technique can identify topological superconductors
Read article: New microscopy technique can identify topological superconductors