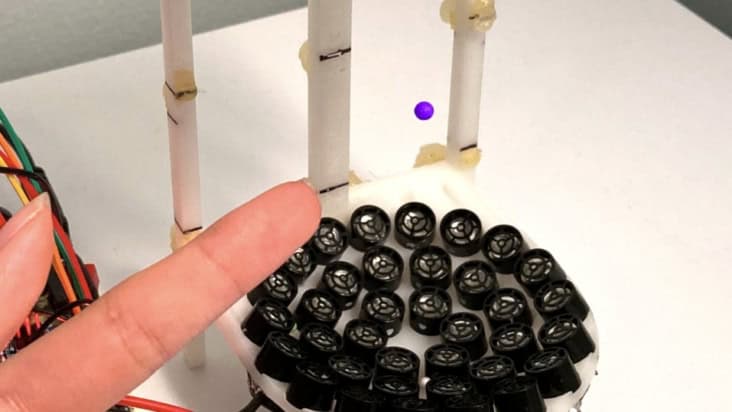


Hidden coated materials could be detected using new technique
Passive system could give quantum sensors a boost
NPL has joined forces with other leading National Metrology Institutes to shape the international standards effort in quantum technologies
Electron undulator amplifies X-ray beam
 Read article: Cavity-based X-ray laser delivers high-quality pulses
Read article: Cavity-based X-ray laser delivers high-quality pulses
Deformed nucleus makes multi-ion design easier
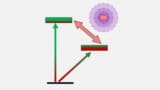 Read article: Ion-clock transition could benefit quantum computing and nuclear physics
Read article: Ion-clock transition could benefit quantum computing and nuclear physics
Device works by monitoring frequency of sound waves propagating through a kagome material
 Read article: New sensor uses topological material to detect helium leaks
Read article: New sensor uses topological material to detect helium leaks
Precision timekeeper is just 5% the size of a conventional clock
 Read article: NPL unveils miniature atomic fountain clock
Read article: NPL unveils miniature atomic fountain clock
New device could be used to observe structures as small as individual proteins, as well as the environment in which they move
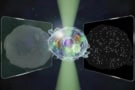 Read article: Bidirectional scattering microscope detects micro- and nanoscale structures simultaneously
Read article: Bidirectional scattering microscope detects micro- and nanoscale structures simultaneously
Finding could have applications in acoustic-levitation-assisted 3D printing, mid-air chemical synthesis and micro-robotics
 Read article: Physicists overcome ‘acoustic collapse’ to levitate multiple objects with sound
Read article: Physicists overcome ‘acoustic collapse’ to levitate multiple objects with sound
Science is done in just about every corner of the globe but many researchers lack access to the cutting-edge instrumentation available at large facilities such as synchrotron light sources and neutron-science centres. Widening this accessibility is an important theme running through this free-to-read briefing.
Devices could eliminate the strong magnetic fields currently required to define the standard unit of resistance
 Read article: Memristors could measure a single quantum of resistance
Read article: Memristors could measure a single quantum of resistance
High-precision laser spectroscopy measurements on the thorium-229 nucleus could reveal new physics, say TU Wien physicists
 Read article: Looking for inconsistencies in the fine structure constant
Read article: Looking for inconsistencies in the fine structure constant
New technique could shed light on electrification of aerosols
 Read article: Electrical charge on objects in optical tweezers can be controlled precisely
Read article: Electrical charge on objects in optical tweezers can be controlled precisely
"Beamforming feedback information" in latest version of the technology can identify individuals passing through radio networks with almost 100% accuracy, say researchers
 Read article: Is your WiFi spying on you?
Read article: Is your WiFi spying on you?
Having more antimatter could help solve profound mysteries of physics
 Read article: Sympathetic cooling gives antihydrogen experiment a boost
Read article: Sympathetic cooling gives antihydrogen experiment a boost
Europe’s largest event for electronics manufacturing comes to Munich on 18−21 November, 2025
 Read article: SEMICON Europa 2025 presents cutting-edge technology for semiconductor R&D and production
Read article: SEMICON Europa 2025 presents cutting-edge technology for semiconductor R&D and production
Research could lead to ultracompact muon sources for applications such as tomography
 Read article: Portable source could produce high-energy muon beams
Read article: Portable source could produce high-energy muon beams
Compact system outperforms astronomical spectrometers
 Read article: Randomly textured lithium niobate gives snapshot spectrometer a boost
Read article: Randomly textured lithium niobate gives snapshot spectrometer a boost
Novel imaging technique can find objects buried within in opaque environments, including biological tissues
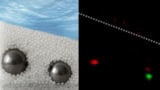 Read article: Fingerprint method can detect objects hidden in complex scattering media
Read article: Fingerprint method can detect objects hidden in complex scattering media
Advanced seismic imaging techniques could improve earthquake early warning models and aid the development of next-generation geothermal power
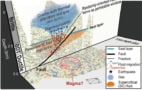 Read article: Scientists obtain detailed maps of earthquake-triggering high-pressure subsurface fluids
Read article: Scientists obtain detailed maps of earthquake-triggering high-pressure subsurface fluids
Global network could pinpoint astronomical sources
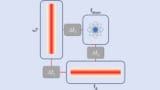 Read article: Phase shift in optical cavities could detect low-frequency gravitational waves
Read article: Phase shift in optical cavities could detect low-frequency gravitational waves
New algorithm turns structured motion into sharper images
 Read article: Motion blur brings a counterintuitive advantage for high-resolution imaging
Read article: Motion blur brings a counterintuitive advantage for high-resolution imaging
With further improvements, the instrument could enable direct tests of relativistic effects
 Read article: Optical gyroscope detects Earth’s rotation with the highest precision yet
Read article: Optical gyroscope detects Earth’s rotation with the highest precision yet
Built on UHV Design’s Production Linear Shift Mechanism range (PLSM), new linear actuator allows heavy objects to be moved very smoothly, says UHV Design engineering director Jon...
 Read article: A low vibration wire scanner fork for free electron lasers
Read article: A low vibration wire scanner fork for free electron lasers
Gabriel Lippmann received the Nobel Prize for Physics in 1908 for a new method of colour photography that was never commercially successful. Margaret Harris finds ...
 Read article: Nobel prizes you’ve never heard of: how an obscure version of colour photography beat quantum theory to the most prestigious prize in physics
Read article: Nobel prizes you’ve never heard of: how an obscure version of colour photography beat quantum theory to the most prestigious prize in physics
Real-time system also detects ebb and flow of tides
 Read article: Cosmic muons monitor river sediments surrounding Shanghai tunnel
Read article: Cosmic muons monitor river sediments surrounding Shanghai tunnel
Machine learning system reduces noise in interferometer mirrors
 Read article: LIGO could observe intermediate-mass black holes using artificial intelligence
Read article: LIGO could observe intermediate-mass black holes using artificial intelligence
Smartphone-based approach could supplement existing seismic detector networks
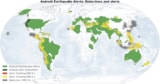 Read article: Android phone network makes an effective early warning system for earthquakes
Read article: Android phone network makes an effective early warning system for earthquakes