
LED could signal silicon laser
A new LED could lead to a silicon-compatible light source
Thank you for registering with Physics World
If you'd like to change your details at any time, please visit My account

A new LED could lead to a silicon-compatible light source

Experiments on B mesons yield puzzling early results
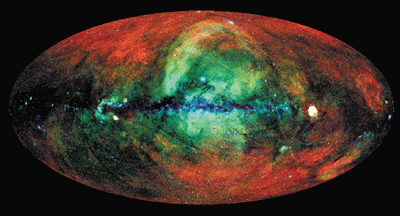 Read article: A reference point to the cosmos
Read article: A reference point to the cosmos
It is a tribute to the dynamism of astrophysics today, and to the achievements of the past century, that Paul Murdin and his distinguished editorial board, together with over 500 contributors, many of them extremely well known astrophysicists, should find it worthwhile to embark on the massive task of creating this encyclopaedia. It is a […]
 Read article: Avalanche physics ploughs ahead
Read article: Avalanche physics ploughs ahead
Numerical models are providing detailed insights into the formation and dynamics of avalanches, explain Perry Barteft and Othmar Buser
 Read article: Getting set for the election
Read article: Getting set for the election
Last month the Royal Society of Chemistry mustered together a collection of like-minded bodies – including the Institute of Physics, the Institute of Biology and the Engineering Council – for the launch of a “charter for science and engineering”. The charter was launched at a meeting at the House of Commons attended by representatives of […]

In the March issue of Physics World, Mike Lockwood of Rutherford Appleton Laboratory and Southampton University, UK, and Duncan H Mackay of the University of St Andrews, UK, underline the significance of the solar magnetic field in our understanding of the solar flux and cosmic rays in particular.

A more detailed review by William Mills of the International Radiation Protection Association and past president of the US Health Physics Society appears in the March issue of Physics World. In Permissible Dose: A History of Radiation Protection in the Twentieth Century, J Samuel Walker, official historian of the NRC, focuses his attention on the […]

In molecular materials like water, the structural units that make up the liquid state can also dictate the properties of the frozen solid. But what about monatomic liquids that are composed of single atoms, rather than molecules? It is tempting to think of such liquids as completely unstructured, like gases in slow motion, but this […]
 Read article: Ultracold plasmas come of age
Read article: Ultracold plasmas come of age
During the past decade, the availability of simple, effective methods for laser cooling and trapping has enabled enormous advances in the experimental study of atoms in their ground state. Until quite recently, however, these techniques have had much less impact on investigations of highly excited atoms – and almost none on plasmas. Several laboratories have […]

Now another observation of atomic and planetary systems behaving in surprisingly similar fashion has been reported by Robert Birtcher and Sandrine Schlutig at Argonne National Laboratory, US, and Stephen Donnelly of Salford University, UK (Phys. Rev. Lett. 2000 85 4968). In the March issue of Physics World, Kai Nordlund of the University of Helsinki in […]