Author
Array
(
[0] => linkedin
[1] => facebook
[2] => twitter
[3] => google-plus
[4] => youtube
)
Array
(
[0] => linkedin
[1] => facebook
[2] => twitter
[3] => google-plus
[4] => youtube
)
Array
(
[0] => linkedin
[1] => facebook
[2] => twitter
[3] => google-plus
[4] => youtube
)
Array
(
[0] => linkedin
[1] => facebook
[2] => twitter
[3] => google-plus
[4] => youtube
)
Array
(
[0] => linkedin
[1] => facebook
[2] => twitter
[3] => google-plus
[4] => youtube
)
No Author
Author archive

Hendrik Schon, Christian Kloc and Batlogg investigated three different acenes: anthracene (which contains three linked rings), tetracene (four) and pentacene (five). The crystals are normally insulating, but when a thin layer of the material was included in a field-effect transistor, it became superconducting. The superconducting transition temperature ranged from 2 Kelvin for pentacene to 4 […]

Bernard Yurke from Lucent Technologies in the US, Andrew Turberfield from Oxford University in the UK and Lucent, and co-workers constructed the tweezers from three separate strands of DNA. DNA molecules are chains of four different bases – adenine, cytosine, guanine and thymine. Adenine will only bind to thymine, and cytosine will only bind to […]

Unlike most experiments at CERN, the £3.2 million Antimatter Decelerator (AD) is designed to slow down particles rather than accelerate them. The antiprotons are created when high-energy protons from the lab’s Proton Synchrotron strike an iridium target. The antiprotons are siphoned off and directed towards the AD, a 188m circumference ring, where they are focussed […]

The Rumba and Tango satellites were sent into space on board a French-Russia launcher. Over the next week they will rendezvous with the Salsa and Samba satellites that were launched on July 16. The four satellites will undergo three months of tests before beginning their two-year scientific mission. Cluster is a joint mission between ESA […]

Georgi, Pati and Quinn were honoured for their “pioneering contributions to the quest for a unified theory of quarks and leptons and the strong, weak and electromagnetic interactions.” Working with Salam, Pati developed the first gauge theory version of the standard model. Working with Sheldon Glashow – who shared the 1979 Nobel Prize for Physics […]
 Read article: New planets and star birth in Manchester
Read article: New planets and star birth in Manchester
A team from the University of Colorado at Boulder will present evidence for what it believes is the youngest massive star cluster ever detected in the Milky Way. It contains about 100 type-O stars, the hottest and most massive stars in our galaxy. Astronomers believe they are less than a million years old. ‘These massive […]

His best-known work was a biography of Einstein, Subtle is the Lord: The Science and the Life of Albert Einstein, which was published in 1982 and won the 1983 American Book Award. Pais went on to publish, among other books, Niels Bohr’s Times in 1991 and Einstein Lived Here in 1994, and completed his autobiography, […]

The so-called ‘complex oxides’ are a group of ceramics with a common chemical formula consisting of two pairs of metallic cations and seven oxygen atoms. Sickafus and co-workers at Los Alamos National Laboratory, Imperial College and the University of Osaka used computer simulations to predict that the relative size of the cation pairs would determine […]
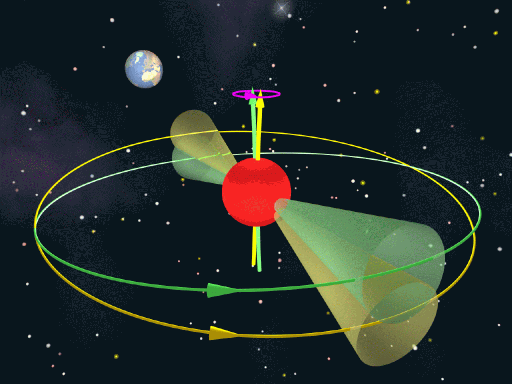 Read article: Wobbling pulsar discovered
Read article: Wobbling pulsar discovered
Pulsars are rotating neutron stars, and are the collapsed cores of supergiant stars that have exploded as supernovae. They are extremely dense, typically 20 km across but with masses a million times greater than the Earth. As a pulsar rotates, it sends beams of radio waves from its magnetic poles out across space, like a […]
 Read article: Brain drains and gains
Read article: Brain drains and gains
Science is a truly international activity: indeed, Einstein told us that the laws of physics are the same everywhere in the universe, not just everywhere on Earth. Mobility between nations has always been a trademark of the physics community, first between the historic university centres of Europe, and later back and forth across the Atlantic. […]
Copyright © 2025 by IOP Publishing Ltd and individual contributors



