Gravitational lensing sheds new light on Hubble constant controversy
Astronomers calculate new value for the universe's expansion
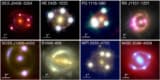 Read article: Gravitational lensing sheds new light on Hubble constant controversy
Read article: Gravitational lensing sheds new light on Hubble constant controversy
Thank you for registering with Physics World
If you'd like to change your details at any time, please visit My account
Isabelle Dumé is a contributing editor to Physics World. She has more than 10 years of experience in science writing and editing in condensed-matter physics relating to technology/nanotechnology/biotechnology, astronomy and astrophysics, energy and the environment, biology and medicine. She has an MSc in advanced materials and a PhD in magnetism. In her spare time, she helps to organize cafés scientifiques.
Astronomers calculate new value for the universe's expansion
 Read article: Gravitational lensing sheds new light on Hubble constant controversy
Read article: Gravitational lensing sheds new light on Hubble constant controversy
Frequency-converted photons are key to proof-of-principle experiment
 Read article: Quantum state teleported between quantum dots at telecoms wavelengths
Read article: Quantum state teleported between quantum dots at telecoms wavelengths
New device could be used to observe structures as small as individual proteins, as well as the environment in which they move
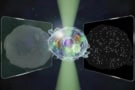 Read article: Bidirectional scattering microscope detects micro- and nanoscale structures simultaneously
Read article: Bidirectional scattering microscope detects micro- and nanoscale structures simultaneously
CMS Collaboration focuses on a family of three all-charm exotic hadrons
 Read article: Tetraquark measurements could shed more light on the strong nuclear force
Read article: Tetraquark measurements could shed more light on the strong nuclear force
Finding could have applications in acoustic-levitation-assisted 3D printing, mid-air chemical synthesis and micro-robotics
 Read article: Physicists overcome ‘acoustic collapse’ to levitate multiple objects with sound
Read article: Physicists overcome ‘acoustic collapse’ to levitate multiple objects with sound
Finding could be important for catalysis and other thermally-activated industrial processes
 Read article: New hybrid state of matter is a mix of solid and liquid
Read article: New hybrid state of matter is a mix of solid and liquid
Fibre-based circuit functions as a programmable router for entangled light
 Read article: Quantum photonics network passes a scaling-up milestone
Read article: Quantum photonics network passes a scaling-up milestone
Discovery of shear-induced bubble formation sheds more light on the divide between eruption and effusion
 Read article: Will this volcano explode, or just ooze? A new mechanism could hold some answers
Read article: Will this volcano explode, or just ooze? A new mechanism could hold some answers
GeV-scale bremsstrahlung from an electron accelerator can be used to produce copper-64 and copper-67
 Read article: Leftover gamma rays produce medically important radioisotopes
Read article: Leftover gamma rays produce medically important radioisotopes
Burst from M-dwarf star could be powerful enough to strip the atmosphere of any planets that orbit it, with implications for the search for extraterrestrial life
 Read article: Astronomers observe a coronal mass ejection from a distant star
Read article: Astronomers observe a coronal mass ejection from a distant star