

Research on the nanoscale has been an active part of physics/chemistry/materials science (take your pick) for more than three decades now. That's ample time for the fruits of this research to start appearing in our daily lives, and indeed, many innovations have already made that transition. But other potential products seem to get stalled in a sort of grey, pre-dawn twilight. This collection explores some of the challenges and opportunities associated with turning advances in nanotechnology into commercial products.
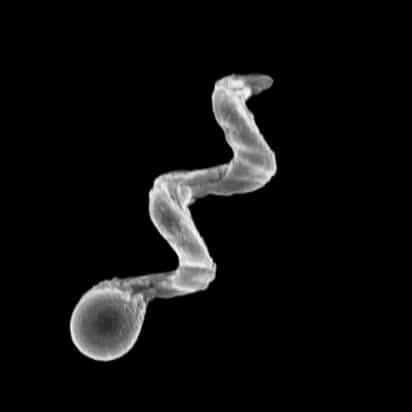
How to make nanoparticles that can "swim" through the body
Graphene Square founder Byung Hee Hong reflects on the different challenges of growing graphene and growing a company
Sheng Chu et al 2017 Nano Futures 1 022001
Read on IOPscienceSiva Krishna Karuturi et al 2018 Nano Futures 2 015004
Read on IOPscienceChloé Minnai et al 2018 Nano Futures 2 011002
Read on IOPscienceP Lourdu Xavier and Arun Richard Chandrasekaran 2018 Nanotechnology 29 062001
Read on IOPscienceEric Auchter et al 2018 Nanotechnology 29 215712
Read on IOPsciencePeize Han et al 2018 Nanotechnology 29 20LT01
Read on IOPscienceThe 2026 edition of Physics World Careers is packed full of advice for early-career scientists. Including a range of valuable advice, informative case studies and recruiter profiles, it demonstrates the variety of jobs that use a physics degree.

Companies seeking to transform innovative materials into products have a range of options, writes Matthew Cohen of venture-capital firm Pangaea Ventures

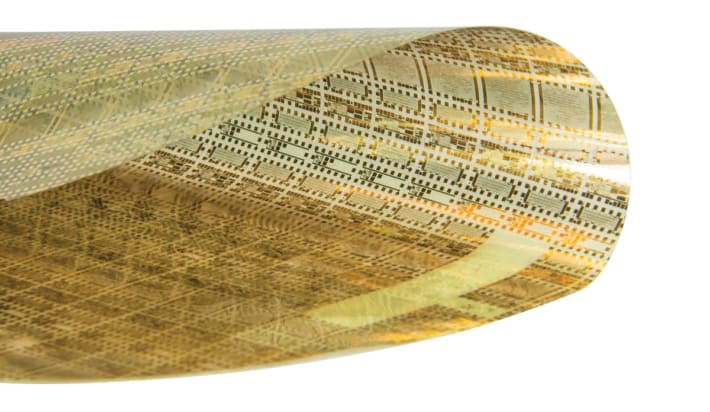
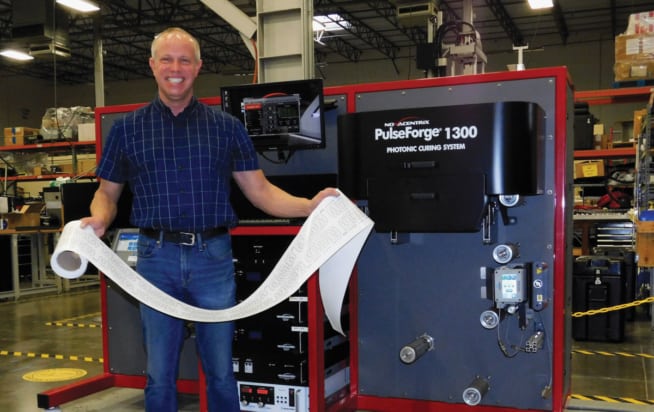
NovaCentrix’s chief technology officer Kurt Schroder on how the company got into printable electronics

Prospects for creating commercial devices based on graphene and other 2D materials
Exploring the process of taking ideas from the lab to the marketplace
A look inside the headquarters of MC10, a spin-off company developing flexible electronics
Jon Cartwright reports on the rival groups creating the darkest substances yet
Mehdi Yazdanpanah describes how he turned $500 and one great idea from his PhD research into a successful small business
New fabric could be used in artificial muscles and smart clothing
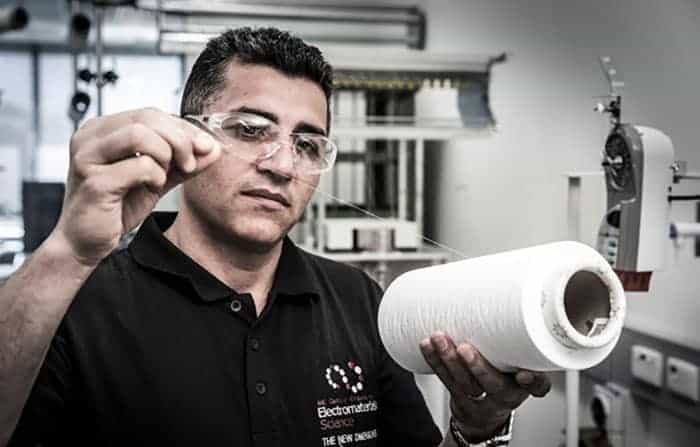 Read article: Knitted nanotubes spin an electromechanical yarn
Read article: Knitted nanotubes spin an electromechanical yarn
Silicon-germanium and extreme ultraviolet lithography keep Moore's law on track
 Read article: Computer-chip features shrink to 7 nm
Read article: Computer-chip features shrink to 7 nm
Devices could someday be used in household appliances
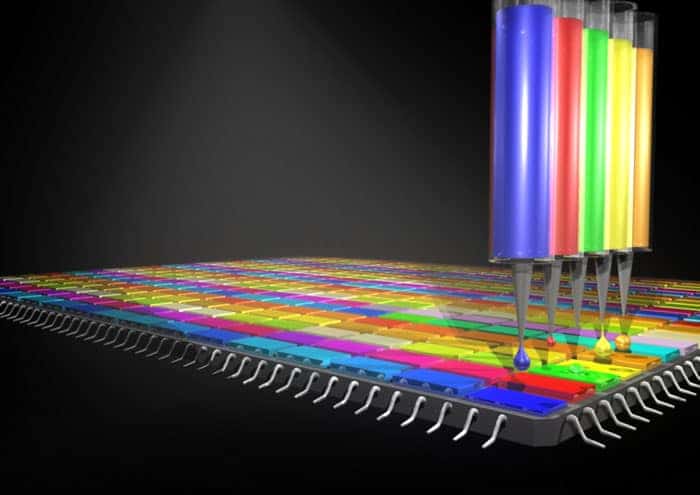 Read article: Spectrometer made from quantum dots is compact and low cost
Read article: Spectrometer made from quantum dots is compact and low cost
Silicon-based device would boost optical bandwidth
 Read article: Infrared detector to free up Internet of tomorrow
Read article: Infrared detector to free up Internet of tomorrow
Technique efficiently cures large industrial parts made of polymeric materials
 Read article: Carbon nanotubes bring aircraft manufacturing out of the oven
Read article: Carbon nanotubes bring aircraft manufacturing out of the oven