Hybrid infrared–optical microscope could improve cancer diagnostics
A simple addition to a conventional microscope allows for all-digital histopathology
 Read article: Hybrid infrared–optical microscope could improve cancer diagnostics
Read article: Hybrid infrared–optical microscope could improve cancer diagnostics
Thank you for registering with Physics World
If you'd like to change your details at any time, please visit My account
Samuel Vennin is a former PhD student contributor to Physics World, working at the intersection between cardiovascular medicine and numerical modelling at Guy's and St Thomas' NHS Foundation Trust, London, UK. He designs new haemodynamic (blood flow and pressure) measurement technologies to assist clinicians in their diagnosis. He holds a PhD in cardiovascular sciences from King's College London, an MSc in biomedical engineering from Imperial College London, and a French engineering degree (MSc equivalent) in electrical engineering from ENSEA.
A simple addition to a conventional microscope allows for all-digital histopathology
 Read article: Hybrid infrared–optical microscope could improve cancer diagnostics
Read article: Hybrid infrared–optical microscope could improve cancer diagnostics
A new sweat sensor can remove the need for blood draws to monitor levels of metabolites
 Read article: Can a simple sweat sensor replace blood tests?
Read article: Can a simple sweat sensor replace blood tests?
Novel biological tool uses blue light to reassemble and activate antibody fragments
 Read article: Blue light activates antibodies on demand
Read article: Blue light activates antibodies on demand
A biocompatible and battery-less pill can noninvasively and accurately sample gut microbiome as it passes through the gastrointestinal tract
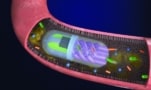 Read article: 3D-printed edible pill can scan the gut microbiome
Read article: 3D-printed edible pill can scan the gut microbiome
Enhanced human blood–brain barrier chip performs in vivo-like drug and antibody transport
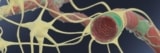 Read article: Human blood–brain barrier engineered on a microchip
Read article: Human blood–brain barrier engineered on a microchip
A machine learning algorithm can read electroencephalograms as well as clinicians
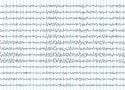 Read article: AI predicts coma outcome from EEG trace
Read article: AI predicts coma outcome from EEG trace
A cavity on top of a microfluidic channel creates a vortex that enables the study of blood and other fluid samples
 Read article: Turning microfluidic devices into mini-centrifuges
Read article: Turning microfluidic devices into mini-centrifuges
Visual and auditory pulses trigger brain waves that sweep away disease-related plaques and restore cognitive abilities in a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease
 Read article: Could light and sound treat Alzheimer’s disease?
Read article: Could light and sound treat Alzheimer’s disease?
Convolutional neural network correctly identifies 96% of tumours of different origins and types
 Read article: AI-based algorithm learns to detect tumours in microscopy images
Read article: AI-based algorithm learns to detect tumours in microscopy images
A flexible patch made from organic LEDs measures reflected light to map oxygen levels in blood
 Read article: Flexible sensor maps blood oxygen levels
Read article: Flexible sensor maps blood oxygen levels
Physics World is now offering early-career scientists the opportunity to work alongside our award-winning journalism team to write and publish news stories for the global scientific community.
We provide training and mentorship to graduate students who are eager to write about the most exciting new research results, and offer them the opportunity to publish their work on a site that’s read by professional scientists all over the world.
Sounds interesting? Find out how you can get involved.