Author
Array
(
[0] => linkedin
[1] => facebook
[2] => twitter
[3] => google-plus
[4] => youtube
)
Array
(
[0] => linkedin
[1] => facebook
[2] => twitter
[3] => google-plus
[4] => youtube
)
Array
(
[0] => linkedin
[1] => facebook
[2] => twitter
[3] => google-plus
[4] => youtube
)
Array
(
[0] => linkedin
[1] => facebook
[2] => twitter
[3] => google-plus
[4] => youtube
)
Array
(
[0] => linkedin
[1] => facebook
[2] => twitter
[3] => google-plus
[4] => youtube
)
No Author
Author archive
 Read article: Chandra delights astronomers
Read article: Chandra delights astronomers
The image of G21.5-0.9, a supernova remnant which is 16,000 light years from Earth, shows a bright central source (the neutron star) with bright nebula and surrounded by a much larger diffuse cloud. The fluffy appearance of the central nebula is thought to be due to magnetic field lines which constrain the motions of the […]

Who do you think will win? Will the prize be awarded for the discovery of the top quark, Bose-Einstein condensation, the gluon, the semiconductor laser, the anisotropy in the cosmic background radiation, the geometric phase, experiments on Bell’s inequalities, neutrino oscillations, giant magnetoresistance, quasicrystals, molecular beam epitaxy, quantum chromodynamics or something else? Please send us […]

Most semiconductor lasers emit light from the edge of the active laser region. However, in the VSCEL geometry light is emitted from the top of the device. This can reduce the threshold current needed to achieve laser action and can improve the optical quality of the output beam. The new device consists of an indium […]

The first evidence for the accelerating universe came from observations of distant supernovae. However, the data were also consistent with an open universe – a universe that would expand forever because the total energy density was less than the so-called critical density – with a low mass density and no cosmological constant. The energy density […]

Brian DeMarco and Deborah Jin used a pair of magneto-optical traps to confine about 700000 atoms of potassium-40 at temperatures below 300 nanokelvin. This is about half of the degeneracy temperature for a gas of fermions. At these temperatures the occupation of the lowest quantum states increases from around zero to about 60%. The quantum […]

Most particle physicists agree on the scientific case for a next-generation linear collider. It is just a question of persuading the politicians to foot the bill

Results presented at the International Europhysics Conference on High Energy Physics in mid-July provide strong hints that the Higgs boson, one of the holy grails of particle physics, is lurking just around the corner. Over 500 physicists gathered in Tampere, Finland, armed with the latest data and hot on the trail of this elusive particle, […]

Many key advances in the biological sciences have been made possible by physics-based techniques. The future of biomedicine depends on collaboration between the two fields
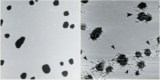 Read article: Single molecules feel the force
Read article: Single molecules feel the force
Biophysicists are now able to study a whole host of living processes with unprecedented accuracy thanks to a microscope normally associated with surface science

“The entire scope of human experience can be viewed as a collective effect resulting from elementary particles dutifully following well-understood equations.” Statements like this excite deep-seated passions and tend to bring out strongly polarized views. The Pearly Gates of Cyberspace by Margaret Wertheim is a product of this passionate debate. This debate is one I […]
Copyright © 2025 by IOP Publishing Ltd and individual contributors
 Read article: Chandra delights astronomers
Read article: Chandra delights astronomers

